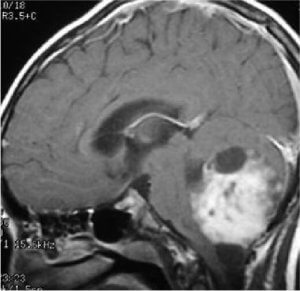
Knowing Brain Tumor
Brain tumor can be classified into primary brain tumors or metastatic/secondary brain tumors. Common benign, primary brain tumors are meningioma and pituitary tumors, and are confined within the brain. Glioma is the most common type of malignant primary brain tumor. Among various types of glioma, glioblastoma is highly aggressive. Patients are typically diagnosed in the prime of their lives .Secondary brain tumors originate from cancer cells arising from other organs, such as the lung, breast and colon etc., and are malignant in nature. Over 75% of such brain tumors are diagnosed in the age of 40 or above. Although compared to other types of cancer, the incidence of brain tumors is relativelylow, but can cause significant disability Annually brain tumor incidence in Hong Kong is around 1000 cases.